By default, access to the AuctionWorx Web API resources requires authentication. That is, a call to a resource via Web API must provide (at a minimum) login credentials or a token.
The AuctionWorx Web API supports two authentication schemes, RWX_BASIC (the default) and RWX_SECURE. This topic describes how to implement and configure each of the schemes by setting the required HTTP headers.
The site's authentication scheme is configured in the root web.config file under the WebAPIAuthScheme key, as shown in the following snippet:
<appSettings> <!--... --> <add key="WebAPIAuthScheme" value="RWX_BASIC"/> </appSettings>
RWX_BASIC is simple to implement. However, RWX_BASIC requires SSL because it sends a username and password (both unencrypted and unhashed) as part of the request's Authentication header. AuctionWorx returns an error if you request resources using RWX_BASIC over an insecure connection (non-SSL).
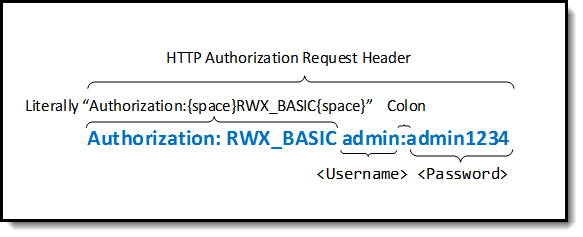
The Authorization header must be set for calls that require authentication/authorization. The “authentication scheme” is the string “RWX_BASIC”. The “authentication credentials” include the requestor’s username, followed by a colon (:), followed by the requestor's password as in
Authorization: RWX_BASIC admin:admin1234
The format is as follows:

The Web API client sample shows one way to generate the RWX_BASIC as part of an HTTP request.
RWX_SECURE authentication is more complex to implement than the RWX_BASIC scheme. RWX_SECURE requires two to four precisely-formatted headers. The benefits of RWX_SECURE include:
Note: Although not required, RWX_SECURE authentication should use SSL since requests and responses could still be intercepted by malicious users.
When RWX_SECURE is set as the value of the WebAPIAuthScheme key in the root web.config file, requests to API Controller methods must be called with the following headers set:
Date
The Date header must be set with the current UTC date/time of the Request in RFC1123 format,for example:
Date: Tue, 15 Nov 1994 08:12:31 GMT
If you cannot set the Date header, you may send the date value in an X-HTTP-Date-Override header instead. AuctionWorx Web API will automatically translate this to Date when requests are received.
X-HTTP-Date-Override: Tue, 15 Nov 1994 08:12:31 GMT
Authorization
The Authorization header must be set for calls that require authentication/authorization.
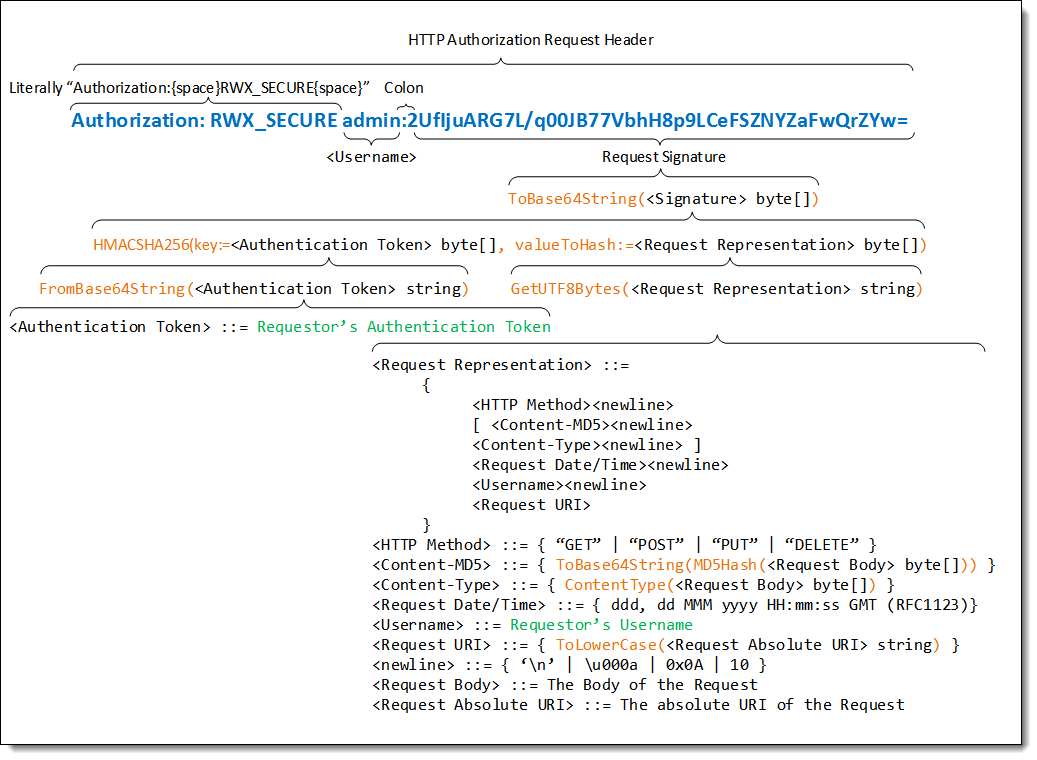
The authentication scheme in the string below is RWX_SECURE. The “authentication credential” is the requestor’s username, followed by a colon character (:), followed by a Request Signature. For example,
Authorization: RWX_SECURE admin:2UfljuARG7L/qOOJB77VbhH8p9LCeFSZNYZaFwQrZYw=
The Request Signature portion of the Authorization header is generated by hashing and concatenation. The generating formula varies depending on whether the Request has a body or no body.
Request Signature for Requests without a Body
Request Signature for Requests with a Body
Content-MD5
The Content-MD5 header is a Base64-encoded binary MD5 sum of the content of the Request Body, and is required only when the Request has a Body. Here's an example of a Content-MD5 header:
Content-MD5: Q2hlY2sgSW50ZWdyaXR5IQ==
Content-Type
The Content-Type header is the MIME type of the Body of the Request, and is required only when the Request has a Body.The following shows the MIME type for a form-based Request:
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
The following graphic helps you visualize the elements and treatments that go into the HTTP Authorization Request header.
Copyright © 2002-2022. RainWorx Software. All rights reserved.